
Miles, J and Shevlin, M (2001) Applying Regression and Correlation: A Guide for Students and Researchers.

Psychometrica Calculators for computing f and d amongst others. SPSS does not calculate Omega squared, so you would have to do this by hand. Kraemer, HC and Thiemann, S (1987) How many subjects? Statistical power analysis in research. In SPSS, you can calculate one-way ANOVAS in two different ways. Jeon, M and De Boeck, P (2017) Decision qualities of Bayes factor and p value-based hypothesis testing. However, in some cases, mostly for the main effects in the MANOVA, I obtained an eta squared that was not covered by the CI: For instance I had F (34, 508) 1.72, partial 2.

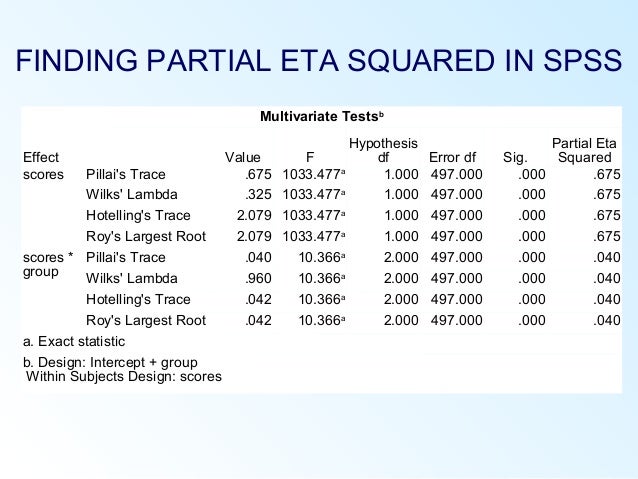
Information Techology, Learning, and Performance Journal 21(1) 1-7. I used the SPSS script to calculate the CIs for eta squared in a MANOVA. Kotrlik, JW and Williams, HA (2003) The incorporation of effect size in information technology, learning, and performance research. Hedges, LV and Olkin I (2016) Overlap Between Treatment and Control Distributions as an Effect Size Measure in Experiments. (1998) Using odds ratios as effect sizes for meta-analysis of dichotomous data: A primer on methods and issues. Using SPSS for Windows:Analyzing and understanding data. Green, SB, Salkind, NJ & Akey, TM (1997). aware that SPSS provides partial estimates of effect size (the proportion. Psychological Methods 1(2) 170-177.įield, A (2013) Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS Statistics. Meta-Analysis of Experiments With Matched Groups or Repeated Measures Designs. The GLM Procedure Dependent Variable: Response. Routledge:New York.ĭunlap, WP, Cortina, JM, Vaslow, JB and Burke, MJ (1996). Figure 39.16 Two-Way Analysis of Variance with Effect Sizes. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.Ĭohen, J, Cohen, P, West, SG and Aiken, LS (2003) Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. Sage Foundation:New York, NY.Ĭohen, J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Valentine (Eds.), The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis (2nd ed., pp. Educational Studies in Mathematics 102 1-8.īorenstein, M (2009) Effect sizes for continuous data. The scales of magnitude for partial $$\omega^text 2) $$ / (expected proportion)īakker, A, Cai, J, English, L, Kaiser, G, Mesa, V and Van Dooren, W (2019) Beyond small, medium, or large: points of consideration when interpreting effect sizes. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates (see also here). Calculating the effect size SPSS does not calculate Eta squared to measure effect size for t-test Calculation t2 Eta squared t2 + (N1 + N2 2) Interpretation values 0.01 Small effect 0.06 Moderate effect 0. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). The scales of magnitude are taken from Cohen, J. The F-test for the corrected model is a test of whether the model as a whole accounts for any variance in the dependent variable.Rules of thumb on magnitudes of effect sizes These are sums of squares around the grand mean as well, and therefore the 'corrected model' SS. It is not given to you by SPSS, but you can use what SPSS provides to calculate it. You have to calculate eta squared yourself. Figure 7.17 : Calculating eta 2 from SPSS output. all the fixed and random factors and covariates and their interactions that are listed on the Between-Subjects table. ignore partial eta squared that SPSS can provide. Figure 7.16: Two-way analysis of variance with moderation in SPSS. The Corrected model SS are sums of squares that can be attributed to the set of all the between-subjects effects, excluding the intercept, i.e. In the case of paired data, this is a measure of the proportion of variance shared by the two variables, and varies from 0 to 1. If you subtracted the grand mean from each observation of the dependent variable and squared that deviation, the sum of these squared deviations would be the Corrected Total SS. A related effect size is r 2, the coefficient of determination (also referred to as R 2 or 'r-squared'), calculated as the square of the Pearson correlation r. The corrected Sums of Squares are the sums of squares around the grand mean of the dependent variable. if you simply squared each value of the dependent variable and summed these squares, you would get the Total SS. The Total Sums of Squares are sums of squares around 0, i.e. Before defining the corrected model, it may be helpful to provide some context for the term "Corrected" by noting that your 'Between-Subjects Effects' table should have rows for each of "Total" and "Corrected Total".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
